Prioritising fuels reduction for water supply protection
Benjamin M. Gannon, Yu Wei, Lee H. MacDonald, Stephanie K. Kampf, Kelly W. Jones, Jeffery B. Cannon, Brett H. Wolk, Antony S. Cheng, Robert N. Addington and Matthew P. Thompson
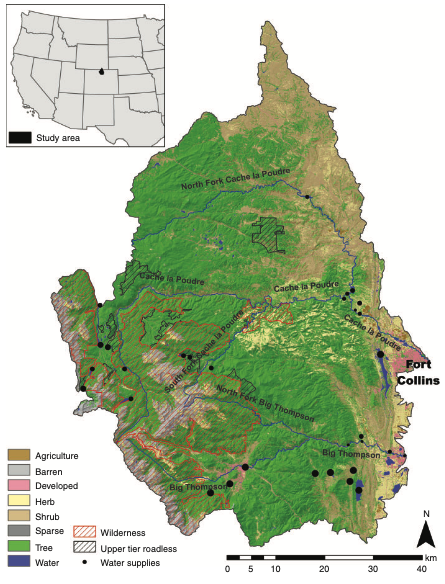
Abstract. Concerns over wildfire impacts to water supplies have motivated efforts to mitigate risk by reducing forest fuels. Methods to assess fuel treatment effects and prioritise their placement are needed to guide risk mitigation efforts. We present a fuel treatment optimisation model to minimise risk to multiple water supplies based on constraints for treatment feasibility and cost. Risk is quantified as the expected sediment impact costs to water supplies by combining measures of fire likelihood and behaviour, erosion, sediment transport and water supply vulnerability. We demonstrate the model’s utility for prioritising fuel treatments in two large watersheds in Colorado, USA, that are critical for municipal water supply. Our results indicate that wildfire risk to water supplies can be substantially reduced by treating a small portion of the watersheds that have dense, fire-prone forests on steep slopes that drain to water supply infrastructure. Our results also show that the cost of fuel treatments outweighs the expected cost savings from reduced sediment inputs owing to the low probability of fuel treatments encountering wildfire and the high cost of thinning forests. This highlights the need to expand use of more cost-effective treatments, like prescribed fire, and to identify fuel treatment projects that benefit multiple resources.